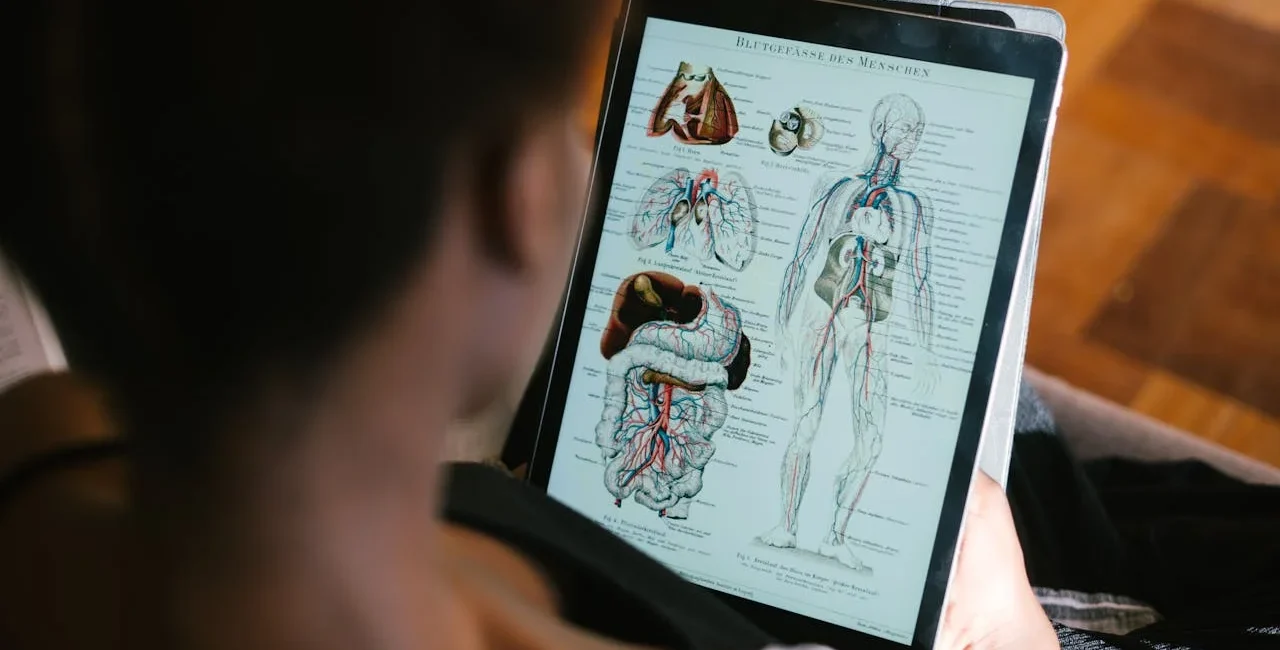
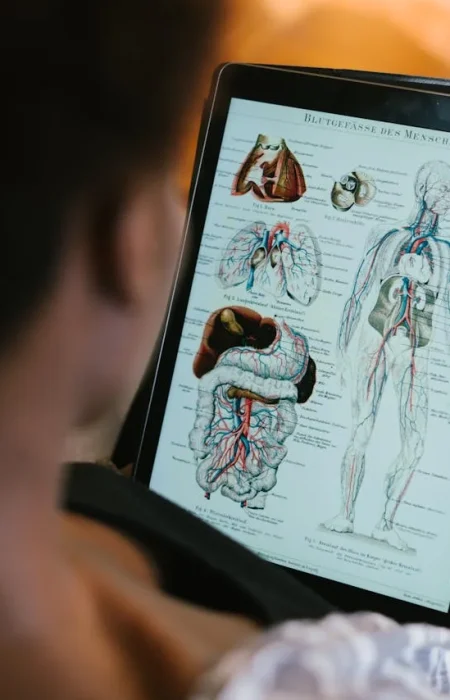
The human body is a marvel of nature, a complex and intricate system that continues to fascinate scientists and laypeople alike. From the way our organs function to the mysteries of our genetic code, there is so much to explore. Here, we present 50 interesting facts about the human body, categorized into five distinct sections to make your journey through human biology both enlightening and enjoyable.
The Brain and Nervous System
- The human brain contains approximately 86 billion neurons.
- Information travels through your nerves at speeds up to 250 mph.
- The brain uses about 20% of the body’s total oxygen supply.
- Your brain can generate 23 watts of electrical power—enough to power a lightbulb.
- We have more synapses in our brain than there are stars in the Milky Way.
- The brain itself feels no pain, although it processes pain signals.
- During sleep, the brain’s cerebrospinal fluid clears out toxins.
- The average attention span of a human is about 8 seconds—shorter than a goldfish.
- The right side of your brain controls the left side of your body and vice versa.
- Your brain’s storage capacity is considered virtually unlimited.
The Skeletal System
- The human body has 206 bones.
- Babies are born with approximately 270 bones, some of which fuse together as they grow.
- The femur, or thigh bone, is the longest and strongest bone in the body.
- The stapes, in the middle ear, is the smallest bone in the body.
- Bones are about five times stronger than steel of the same density.
- Bone is a living tissue that constantly regenerates.
- The hand has 27 bones, more than any other part of the body.
- Your bones make up about 14% of your total body weight.
- The human skull is made up of 22 bones.
- Bones are composed of 31% water.
The Circulatory System
- The heart beats approximately 100,000 times a day.
- Blood travels around 12,000 miles through your body each day.
- The human body contains about 1.5 gallons of blood.
- Red blood cells take about 20 seconds to circulate through the entire body.
- The heart can continue to beat even when disconnected from the body.
- Capillaries are so small that red blood cells must travel through them in single file.
- The aorta is the largest artery in the body.
- The heart pumps about 2,000 gallons of blood each day.
- There are about 60,000 miles of blood vessels in the human body.
- Blood makes up about 7-8% of your total body weight.
The Digestive System
- The average person produces about 1-1.5 liters of saliva each day.
- The stomach’s digestive acids are strong enough to dissolve zinc.
- Your stomach lining regenerates every few days to prevent it from digesting itself.
- The small intestine is about 20 feet long.
- It takes about 6-8 hours for food to pass through the stomach and small intestine.
- The liver performs over 500 functions in the body.
- The large intestine is about 5 feet long.
- The human body can produce over a liter of mucus per day.
- The tongue is covered with about 8,000 taste buds.
- The human gut contains around 100 trillion bacteria.
The Muscular System
- The human body has over 600 muscles.
- The gluteus maximus is the largest muscle in the body.
- The stapedius, in the middle ear, is the smallest muscle.
- Muscles account for about 40% of your total body weight.
- The strongest muscle based on its size is the masseter, or jaw muscle.
- The muscles in your eyes make around 100,000 movements a day.
- It takes 17 muscles to smile and 43 to frown.
- The heart is the hardest-working muscle, pumping continuously.
- Muscle fibers are thinner than a human hair but can support up to 1,000 times their weight.
- Your muscles are capable of pulling with the force of about 25 tons.
Conclusion
The human body is an extraordinary machine, capable of amazing feats and intricate processes that keep us alive and functioning every day. From our powerful brains to our resilient bones and dynamic muscles, every part plays a crucial role in our overall well-being. These 50 facts barely scratch the surface, but they offer a glimpse into the incredible world within us. Whether you’re a science enthusiast or just curious about how your body works, there’s always more to discover about the human body.